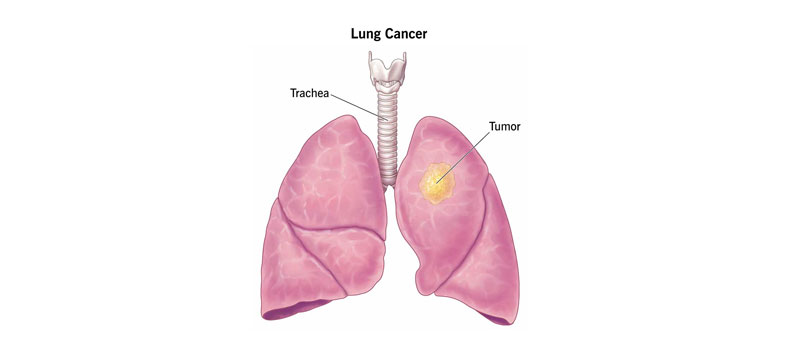
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most common and serious forms of cancer worldwide. It occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the tissues of the lungs. The two main types are Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), which accounts for the majority of cases, and Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC), which is more aggressive and fast-spreading. Smoking is the leading cause, but lung cancer can also develop in non-smokers due to factors like air pollution, genetic predisposition, and exposure to harmful chemicals. Early detection plays a crucial role in improving treatment outcomes. Common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, depending on the type and stage of the disease.
- Two main types: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
- Primary cause: Smoking (both active and passive)
- Other causes: Air pollution, genetic factors, and occupational exposure (e.g., asbestos)
- Common symptoms: Persistent cough, coughing up blood, breathlessness, chest pain, and unexplained weight loss
- Diagnostic tools: CT Scan, PET-CT, Bronchoscopy, Biopsy
